Normal Poop Guide: 7 Steps for Healthy Stool
- What Is a Normal Poop?
- What Poop Color, Smell Mean
- Common Causes of Abnormal Poop
- 7 Steps to Get Your Poop Back to Normal

Are you wondering if your poop is considered “normal”? Most of us have asked ourselves this question at some point.
When you don’t have regular bowel movements or your feces has an unusual color and/or consistency, it can definitely indicate that something isn’t quite right. There are many reasons why you might not be pooping regularly, such as your stool color. Maybe you ate too much spicy food, are sick with a virus, you’re dehydrated, or you could have a more serious underlying digestive disease or illness.
If you’re curious about whether your pooping habits are healthy, then you’re already on the right track. The frequency, color, shape, size, and consistency of your poop can actually tell you a lot about the health of your entire body. For example, green poop, which is a common health problem among children and some adults with diarrhea, can indicate that something you ate isn’t agreeing with you. Constipation may be due to a poor diet lacking fiber, high amounts of stress, or something hormone-related like your menstrual cycle or pregnancy.
Below, we’ll cover in much more detail what a normal poop should look like, how often you should be pooping, and what the smell and color of your stool can tell you.
What Is a Normal Poop?
Poop (feces) is defined as waste matter that is discharged/excreted from the bowels after food has been digested. Simply put, poop is the body’s natural way of expelling the leftover waste and toxins that it doesn’t need after it has absorbed all the usable nutrients from the foods you eat.
Defecation is another term for pooping, which means the discharge of feces from the body.
The process of digestion – eating a food, the food traveling through your stomach and intestines, making its way down to your colon and anal canal, and then you pooping out the digested waste – involves many different aspects of your body. For example, digestive enzymes, hormones, blood flow, muscle contractions, and more are all involved in the pooping process.
When even one of these is off, your digestion suffers greatly – and this shows up in your poop.
How Many Times per Day Should I Poop?
Going too often or not often enough is not considered normal. Having trouble going to the bathroom more than a few times a week or going too many times per day (more than three) is considered by most experts to be a sign of abnormal bowel movements.
The amount of bowel movements a day that someone should have varies from person to person, so there is not one specific number that is considered completely “normal.” However, most experts agree that it’s important to go to the bathroom at least three or more times per week at a minimum. Any less than this indicates that you are constipated.
Generally, going once or twice a day is considered normal. Going every other day is also somewhat normal, as long as you feel comfortable and do not experience pain in your abdomen.
It may be normal for one person to poop two times per day and for another person to poop just once every other day. Above all else, you want to make sure things are pretty consistent from day to day. This shows you what is “normal” poop for your own body and clues you in to when something internally is off.
What Should My Poop Look Like?
When you do go to the bathroom, it’s ideal to have a poop that is all connected in one long, smooth “S” shape. Poops like this develop when you eat enough fiber and drink plenty of water or other hydrating liquids, which lubricates your bowels.
However, a smooth poop that is thin or broken up into a few smaller poops is not something to be concerned about, according to digestive experts, as long as this is “normal” for you and does not cause you any discomfort.
In terms of color, the color of a normal poop should be a medium to dark brown. Sometimes you may have green poop if you consume green foods, such as lots of leafy green vegetables, and this is considered normal.
You may have heard of the the Bristol Stool Chart in the past, which was designed in the 1990s to be a medical aid that classifies poop into one of seven categories. When physicians meet with patients and discuss their digestive health, they can use the Bristol chart to locate the patient’s typical poop and learn what may be causing a problem.
The idea behind designing the scale was to classify how poop looks depending on the time that it takes for the poop to form in the colon, or the poop’s “transit time.” If a poop is considered abnormal, it usually falls into categories 1-2 (which are signs of constipation and poop being held too long in the body) or categories 6-7 (which are signs of diarrhea and the poop moving too quickly through the body).
According to the Bristol Stool Chart, the seven types of stool are:
- Type 1: Separate hard lumps, like nuts (hard to pass)
- Type 2: Sausage-shaped but lumpy
- Type 3: Like a sausage but with cracks on the surface
- Type 4: Like a sausage or snake, smooth and soft
- Type 5: Soft blobs with clear-cut edges (passed easily)
- Type 6: Fluffy pieces with ragged edges, a mushy stool
- Type 7: Watery, no solid pieces, entirely liquid
Types 1-2: Indicates constipation. (3)
Types 3-5: Considered to be ideal (especially 4), normal poops.
Type 6-7: Considered abnormal and indicates diarrhea.
How Long Should a Normal Poop Take?
A healthy poop doesn’t cause pain, break up into multiple little pieces, or take a very long time and lots of pushing to come out. It should feel pretty easy to produce a poop, and you should feel like you’ve emptied your intestines once you’re done going.
The whole process should not take more than several minutes for most people or ideally even shorter. In fact, one study found evidence that most mammals, regardless of their size, produce bowel movements in about 12 seconds (give or take about seven seconds)!
It’s not normal to experience lots of straining, pressure and pain while passing a bowel movement. Poop should not cause too much pressure or burning, cause you to bleed, or require a lot of pushing and effort on your part.
If you have to push very hard to poop and notice blood, you are likely experiencing hemorrhoids. While these are usually not very serious and do not require medical attention, they can be painful.
You also shouldn’t experience too many changes in your poop’s consistency and how long it takes you to go. If your poop is either overly watery or very hard and difficult to push out, this is a sign that things are not going well in your digestive tract.
Diarrhea produces overly soft or watery poops and can be dangerous if it persists because it dehydrates and weakens the body. It might also cause your poop to be green.
What does it mean when your stomach hurts and your poop is green? The causes of diarrhea and green poop vary, but often the reasons are dehydration, a viral stomach flu or infection, as a result of eating something with harmful parasites or bacteria, or even nerves.
Diarrhea and the sudden urge to poop can also be caused by certain medications or medical conditions, such as:
- gluten sensitivity or celiac disease (a gluten allergy)
- lactose intolerance (a dairy food allergy)
- inflammatory bowel diseases, like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
- leaky gut syndrome
This is why it’s very important to see a physician if you experience diarrhea on an ongoing basis.
Constipation on the other hand is categorized by infrequent, usually painful poops that are caused by slow colonic transit or dysfunction in the pelvic floor. Many people experience ongoing chronic constipation – in fact, this is one of the most reported problems at doctor visits every year.
Constipation can also be accompanied by other digestive symptoms, like flatulence (gas), abdominal pain, stomach bloating and loss of appetite. It can be caused by many different factors depending on the individual.
How Bad Is It to Hold in Your Poop?
Because you might not have access to a bathroom 24/7 or feel comfortable pooping in certain places, you might need to hold in your poop from time to time. Doing this occasionally isn’t a big deal, but you don’t want to make a habit of it.
Holding in your poop can put added pressure on your bowels and colon, potentially even leading them to change shape slightly if you do this often enough. It may also contribute to constipation and straining when you do finally poop because it causes your stools to further bulk up.
Over time, if you regularly ignore your urge to poop, you might stop responding to the urge as well. The muscles that control your bowels may stop working properly, leading to more constipation.
Try to honor your body and poop when you need to, avoiding holding it in for more than several minutes if possible.
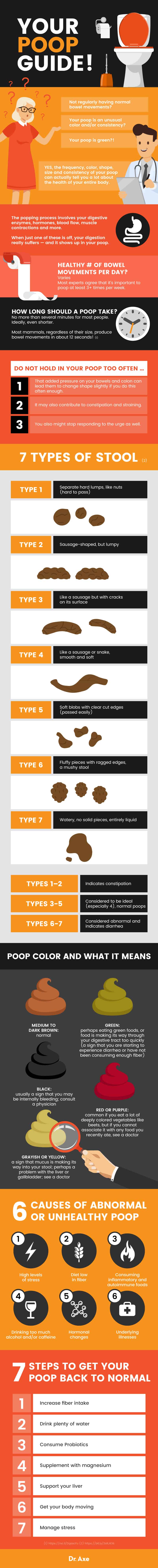
What Poop Color, Smell Mean
Facts About Poop Color:
Stool color is determined by what you eat and the amount of bile enzymes you produce. Bile is a yellow-green fluid that mostly helps you digest fats in your diet. It can change the color of your poop during the digestive process due to how enzymes impact pigments in your stool.
As mentioned above, the color of a normal poop should usually be a medium to dark brown. However, occasionally having green poop is also common and not a problem.
Experiencing poops that are black, gray, yellow, white or red in color can be a sign that something deeper is wrong. If you have green poop along with other symptoms, like stomachaches and diarrhea, this is also problematic.
- Green poop can sometimes be a common problem among both children and, to a lesser extent, adults. Why is your poop green, and what health problems can cause green poop? If you haven’t recently eaten anything green, green-colored poops might mean that food is making its way through your digestive tract very quickly, which can be a sign that you are starting to experience diarrhea or have not been consuming enough fiber to slow the transition down within your digestive tract.
- What foods can give you green poop? These include green leafy vegetables, like spinach or kale, vegetables juices, blueberries, pistachios, green food powders, foods that contain green food coloring, and also sometimes iron supplements.
- In infants, the color and consistency of stool differs according to the type of formula they are given or if they are breastfed. Babies fed formula may also deal with harder stools/more constipation compared to breastfed babies. When babies start eating solid foods, certain veggies or fruits might cause green poop in babies.
Other than green poops, there are also other reasons you might develop abnormal stool colors. For example, you may have blood in your stool or mucus in your poop.
- Black poops usually a sign that you may be internally bleeding, so if this persists for more than two to three poops, you want to consult a physician.
- Red or purple poop can be somewhat common if you eat a lot of deeply colored vegetables, like beets, but if you experience colors like this that you cannot associate with any food you recently ate, you want to keep an eye on how many days it lasts and possibly see a doctor.
- Blood in stool can result in black poop or bright red blood in poop, which may be a symptom of bleeding from the anus (also called rectal bleeding). Blood in stool is also referred to medically as hematochezia, which can be caused by bleeding stomach ulcers, blood supply being cut off to part of the intestines, gastritis, anal fissures, bowel ischemia, diverticulosis, hemorrhoids (often the cause of bright red blood), infection in the intestines, inflammatory bowel diseases, and polyps or cancer in the colon or small intestine.
- Poop that is grayish or yellow in color is normally a sign that mucus is making its way into your stool. This shows that likely there is a problem with the liver or gallbladder, since the liver is responsible for producing bile that gives stool a grayish/yellow tint.
- Mucus in your stools can cause you to pass “stringy poops” that appear to contain a jelly-like substance, which is made by the body to keep the lining of your colon moist and lubricated. What are some causes of mucus in poop? These can include Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and even colorectal cancer.
- A small amount of mucus in your poop is not a big deal or a sign of a problem, but a lot is not normal. If you notice mucus in your poop, blood, abdominal pain and diarrhea happening at the same time, head to your doctor for an evaluation.
Facts About Poop Smell:
Although it may sound unpleasant, your poop smelling is actually not a bad thing or an indication of poor health. Poop smells because of the toxins it helps draw out of your body and because of the bacteria involved in the gut lining.
There is not any specific poop smell that is considered “normal.” Again, it’s just important to keep an eye on things being consistent and comfortable.
If you do notice a sudden change in the smell of your poop – from “not so great” to “very, very bad” – this could be a sign that something more serious is taking place within your gut. If the smell continues for several days, you may want to consult your doctor, who may recommend a colonoscopy if needed.
Common Causes of Abnormal Poop
1. High Levels of Stress
According to a report published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology,
Psychological stress is an important factor for the development of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) … psychological stresses have marked impact on intestinal sensitivity, motility, secretion and permeability, and the underlying mechanism has a close correlation with mucosal immune activation, alterations in central nervous system, peripheral neurons and gastrointestinal microbiota.
Chronic stress makes it difficult for many people to relax their bodies and go to the bathroom properly. Your brain and gut actually have a very close relationship. They communicate how you are feeling back and forth to each other, working to increase and decrease “stress hormones” depending on your moods, which play a big part in healthy digestion.
In fact, common digestive disorders like IBS are closely correlated with high levels of stress. When we feel stressed, the brain communicates these uneasy feelings to the digestive tract, making it very common for the gut wall to either constrict and tense up (causing constipation) or to work overtime and cramp up (causing diarrhea).
Stress can sometimes be a huge digestive obstacle to overcome, so much so that you may already eat a healthy diet and drink plenty of water, but without also addressing high stress levels, you still can’t experience digestive relief. While you may not be able to control things like a busy schedule, you can prioritize reducing your stress by making sure you get good sleep each night and by regularly exercising, both of which help bring down stress hormones levels.
2. Diet Low in Fiber
Fiber is extremely important when it comes to healthy poops. It is the binding substance that gives poop its form and helps it move through the digestive tract.
There are two kinds of fiber, both of which play a role in creating healthy poops: insoluble and soluble fiber. The difference between the two is their ability to dissolve in water. Soluble fiber is able to dissolve in water while insoluble fiber is not.
If you struggle with ongoing constipation, pay close attention to how much fiber you consume daily. Consider swapping some of the foods in your diet that lack fiber – like meat, cheese, refined carbohydrates and hydrogenated oils – for much healthier, whole foods that provide your body with a lot more benefits. (You’ll find a list of these foods below.)
3. Inflammatory and Autoimmune Foods
Unfortunately, many people consume common inflammatory and allergen foods on a frequent basis, and these can really mess with the digestive system’s ability to produce normal poops, in addition to creating more serious conditions like leaky gut syndrome and autoimmune disease. If you’re




